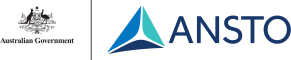
70+ Years of ANSTO
ANSTO celebrates 40 years of irradiating silicon
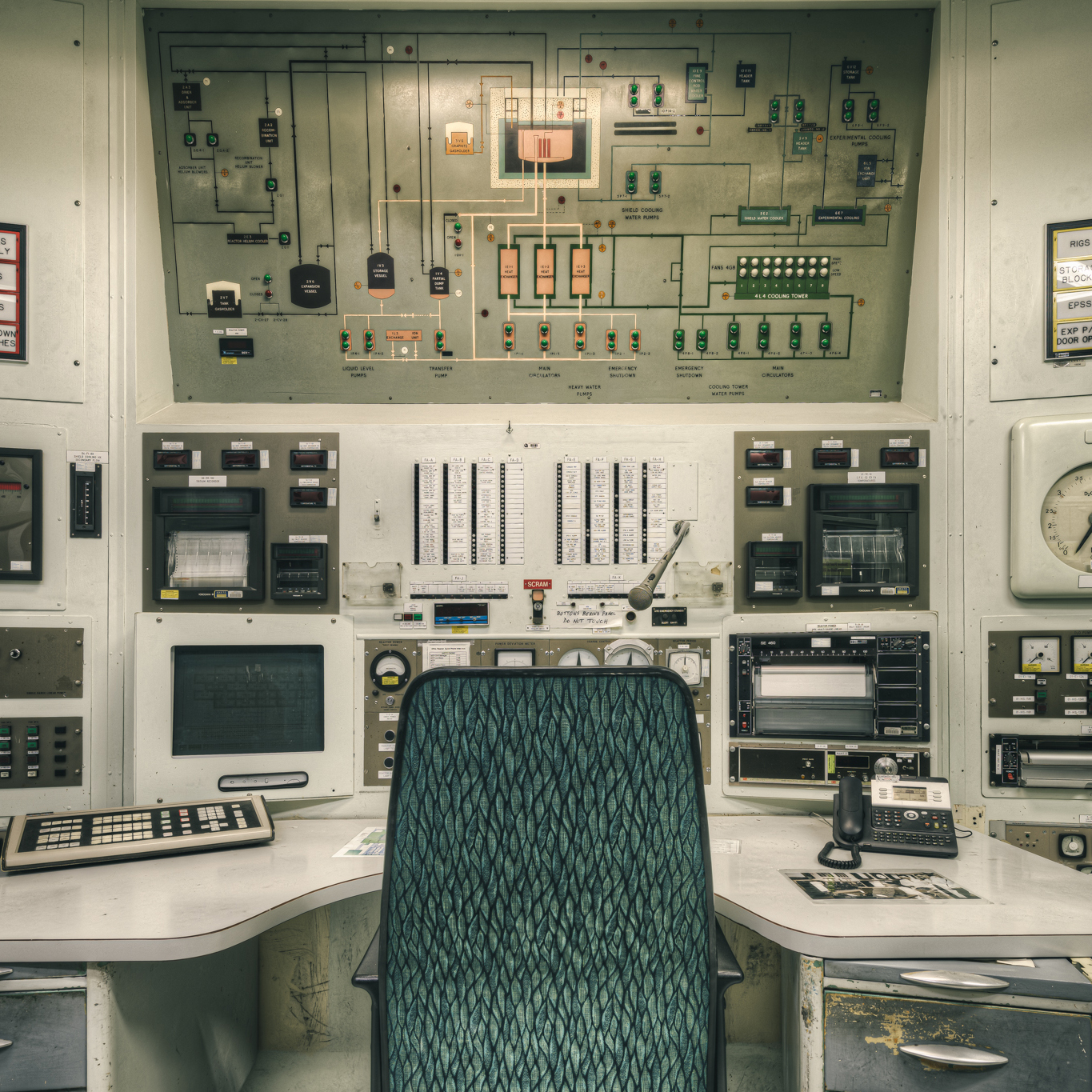

Decommissioning of HIFAR reactor commences

Australian Synchrotron goes green with 3,200 rooftop solar panels installed

Cold Neutron Source (CNS) replaced in OPAL reactor
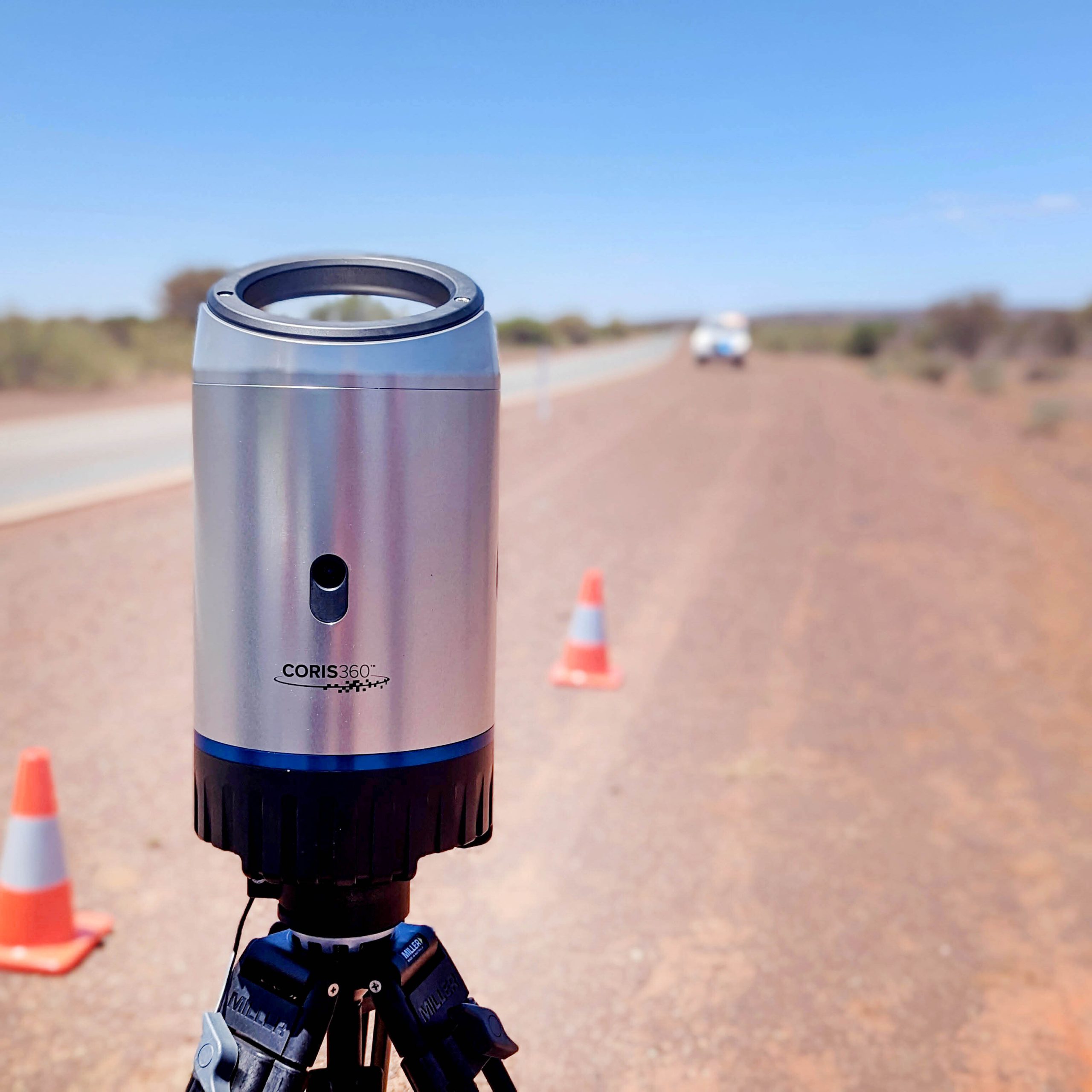

Finding missing radioactive capsule in outback Western Australia

ANSTO becomes part of the Critical Minerals Hub
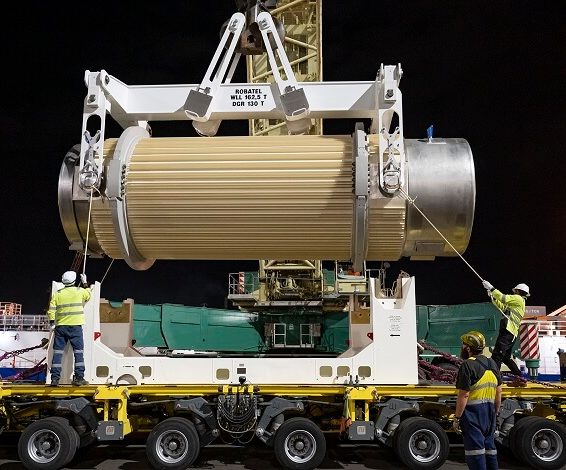

Second repatriation of Intermediate level waste back to Australia
ANSTO irradiates 50% of the global supply of silicon for high end electronics and renewable energy sources
OPAL reactor review with IAEA top marks
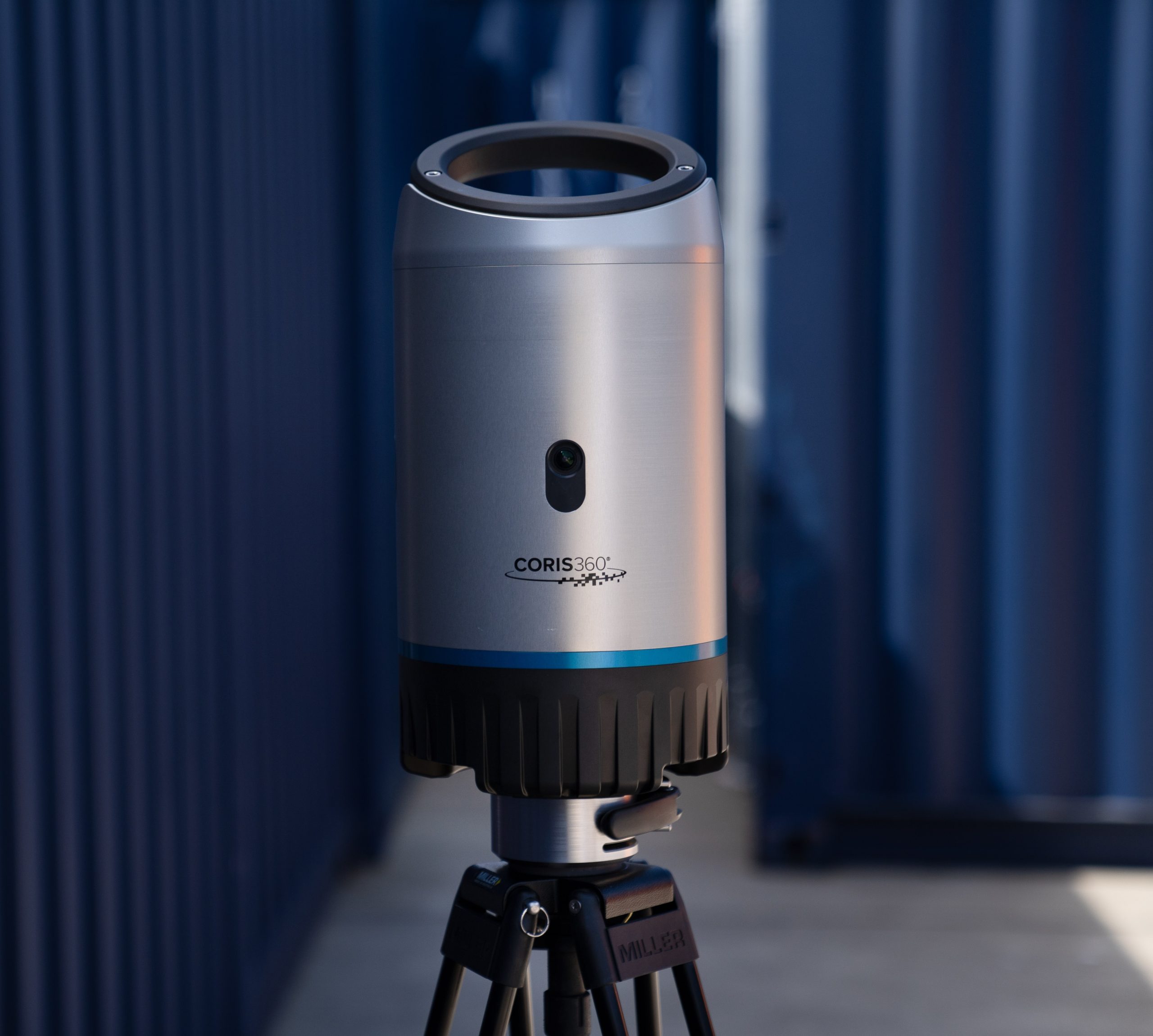

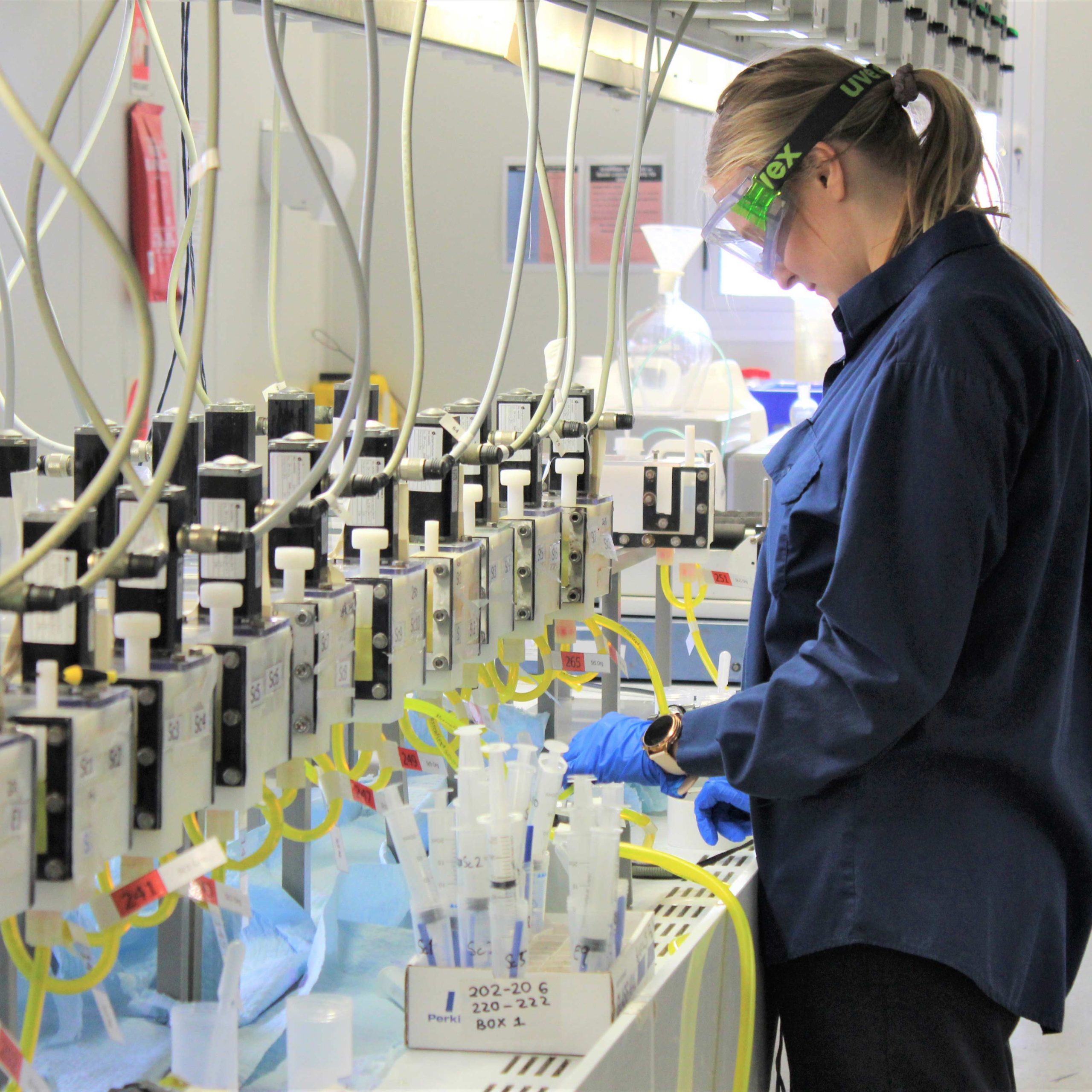
CORIS360®advanced radiation imaging solution developed
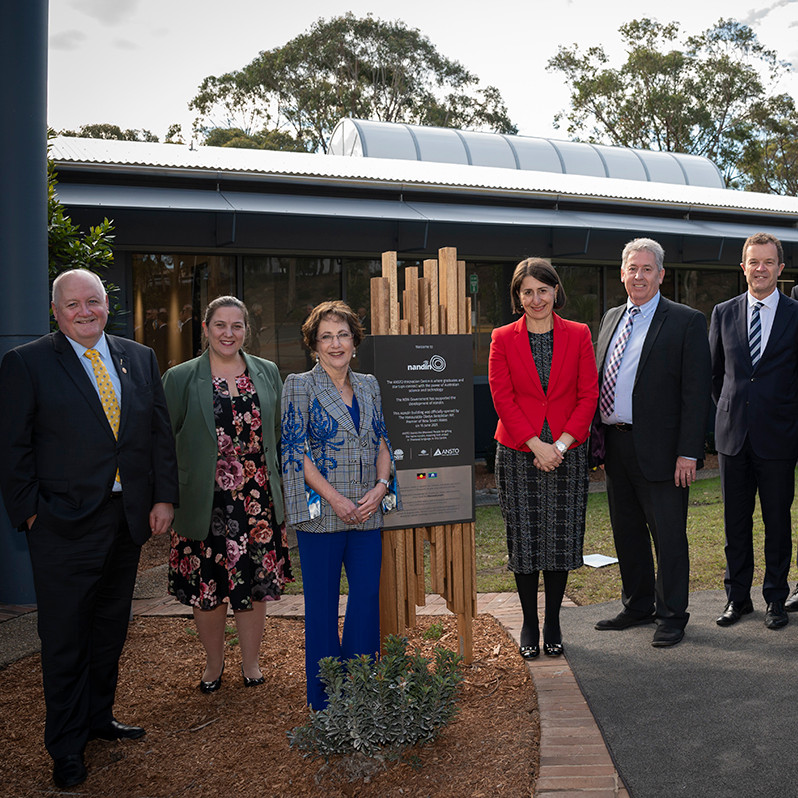

Nandin innovation centre is established

Syroc demonstration plant
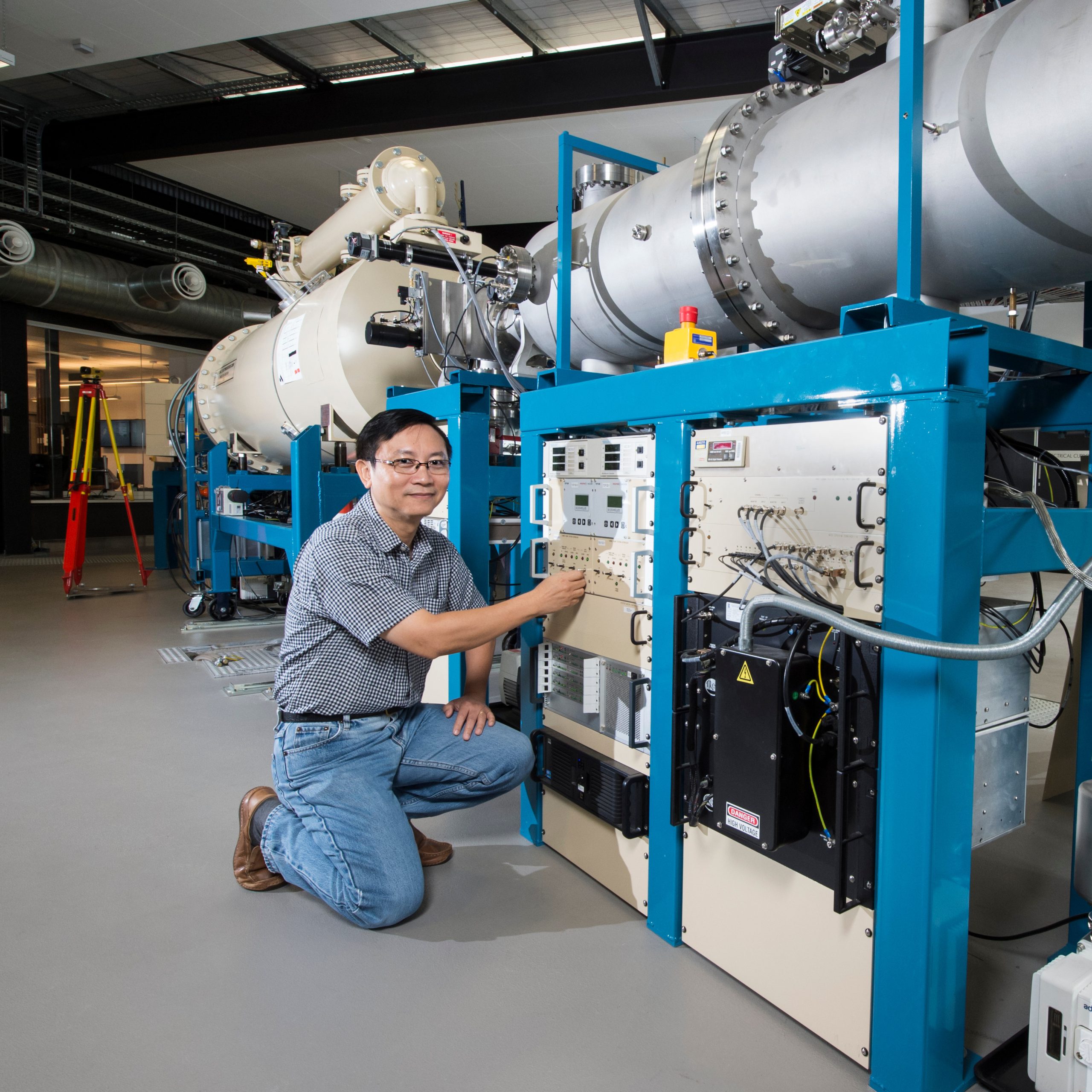
CAS received its first two orders for MABI units from IAEA
Food provenance research
ANSTO Supports clinical trial for Lu 177 as a new cancer treatment
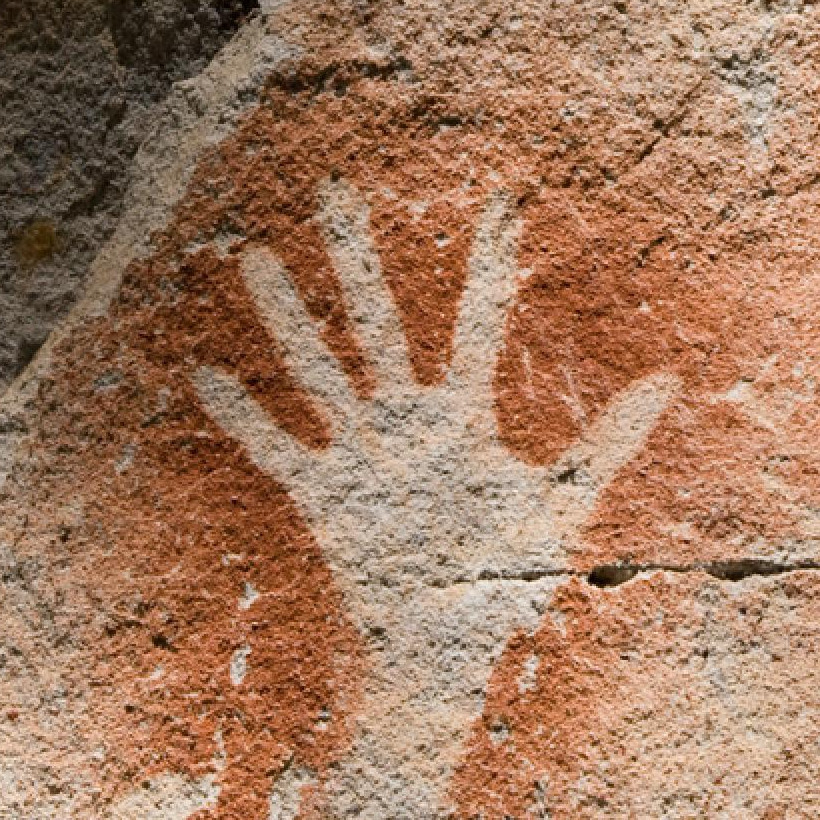

Carbon dating used to support Aboriginal cultural heritage
First repatriation of Intermediate Level Waste back to Australia
ARPANSA licence granted (F0280) for routine operation of VEGA Accelerator
ARPANSA give approval for the operation of VEGA the 1MV AMS machine
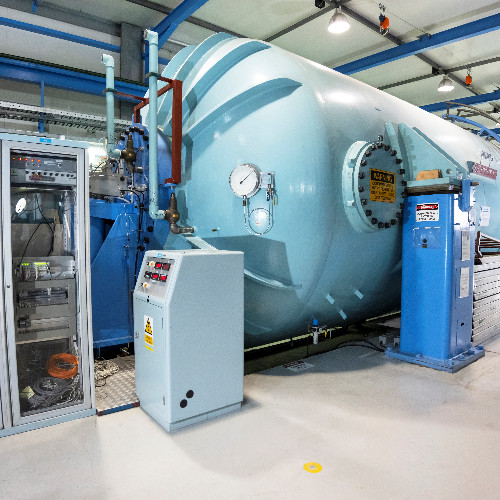

The second of two new particle accelerators are installed at ANSTO as part of a $38 Million investment for the Centre for Accelerator Science
New $10M JR Bird Building B53 which houses the new CAS accelerators is now essentially complete and being used by accelerator and NEC staff
ANSTO contribute to the IPPC report on climate change using accelerator science
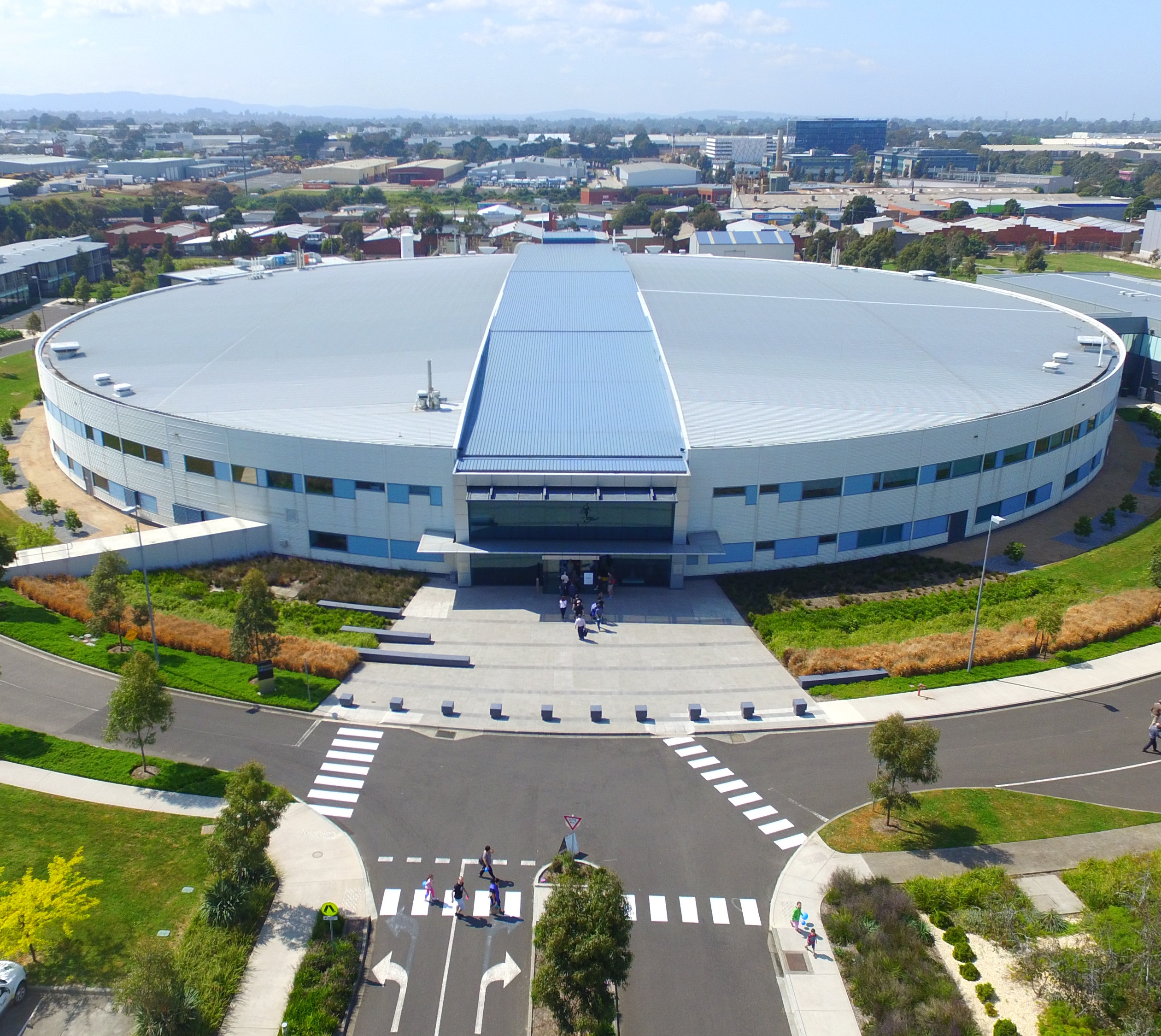

The Australian Synchrotron becomes part of ANSTO
ANSTO CIC approved $38M for new CAS building ($20.4M) and two new accelerators
ANSTO Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear science support water resource management

Budget announcement of $25M for CAS and $37M for more neutron beamlines on OPAL in Bragg
Moata reactor decommissioned
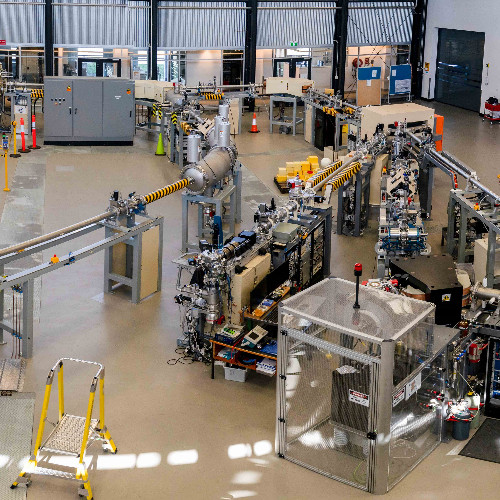

Centre for Accelerator Science (CAS)
Australian Synchrotron operations commenced with five beamlines in operation
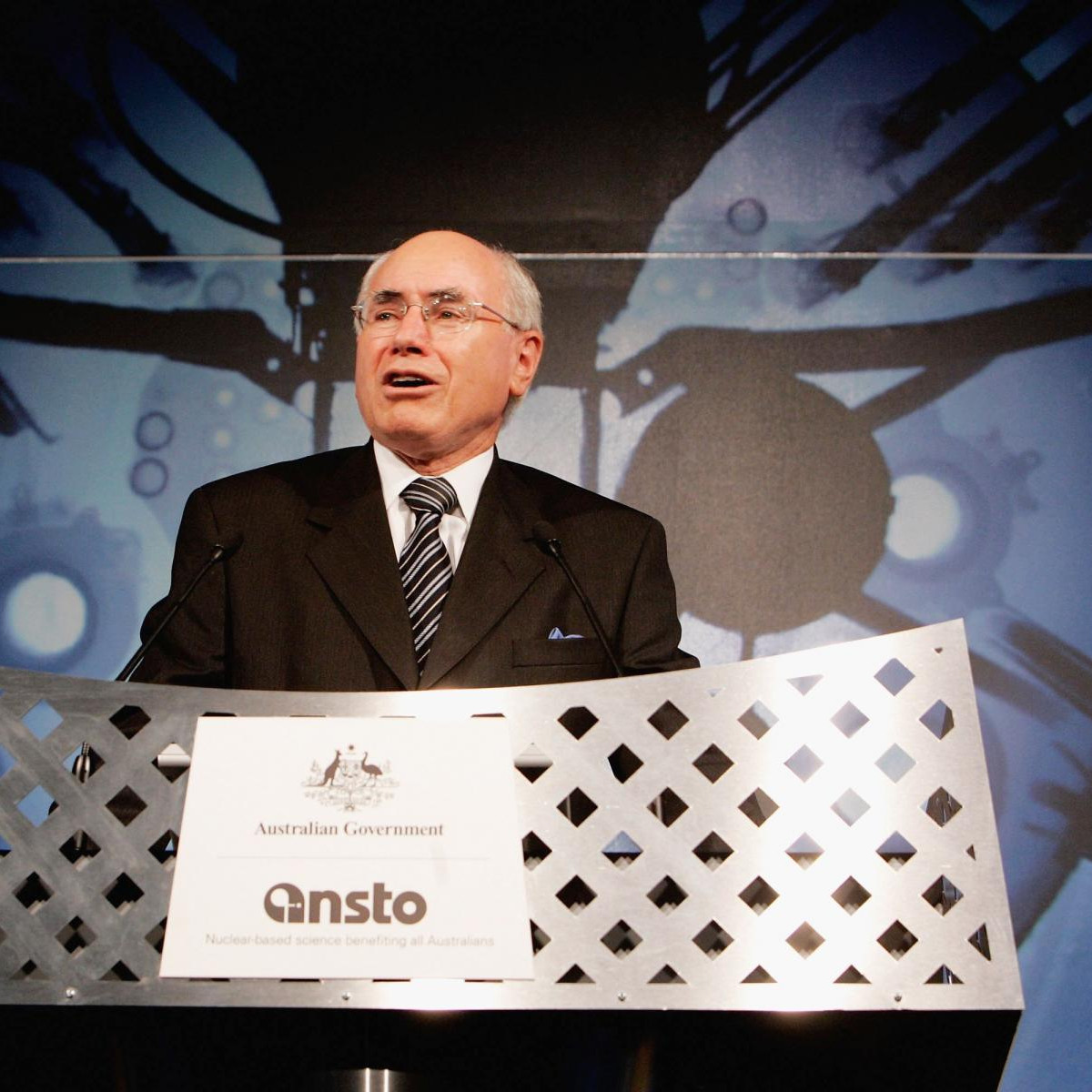

John Howard officiates the opening of the OPAL research reactor
Australian Synchrotron project reached a major milestone with engineers and scientists achieving ‘first light’
Guide hall for neutron scattering

Minister Brendan Nelson opens STAR
ARPANSA issues an operational licence for STAR
ACNS Founded as the Bragg Institute
2MV machine with both IBA and AMS capabilities to replace the 3MV Van de Graaff
ANSTO had constructed up to 54 air sampling units and analysed over 16,000 ASP filter samples using IBA techniques.

First 10Be measurements done on ANTARES

5 year IAEA/ CRP with 18 countries to study global ambient air pollution using nuclear techniques.
First 14C dating measurements done on ANTARES

David Garton ran the first ASP unit at the AAEC weather station
Critical Facility (ANSTO Building 53) Tandem Hall construction finished
First sod turned on Tandem Hall construction
Rutgers Tandem accelerator purchased
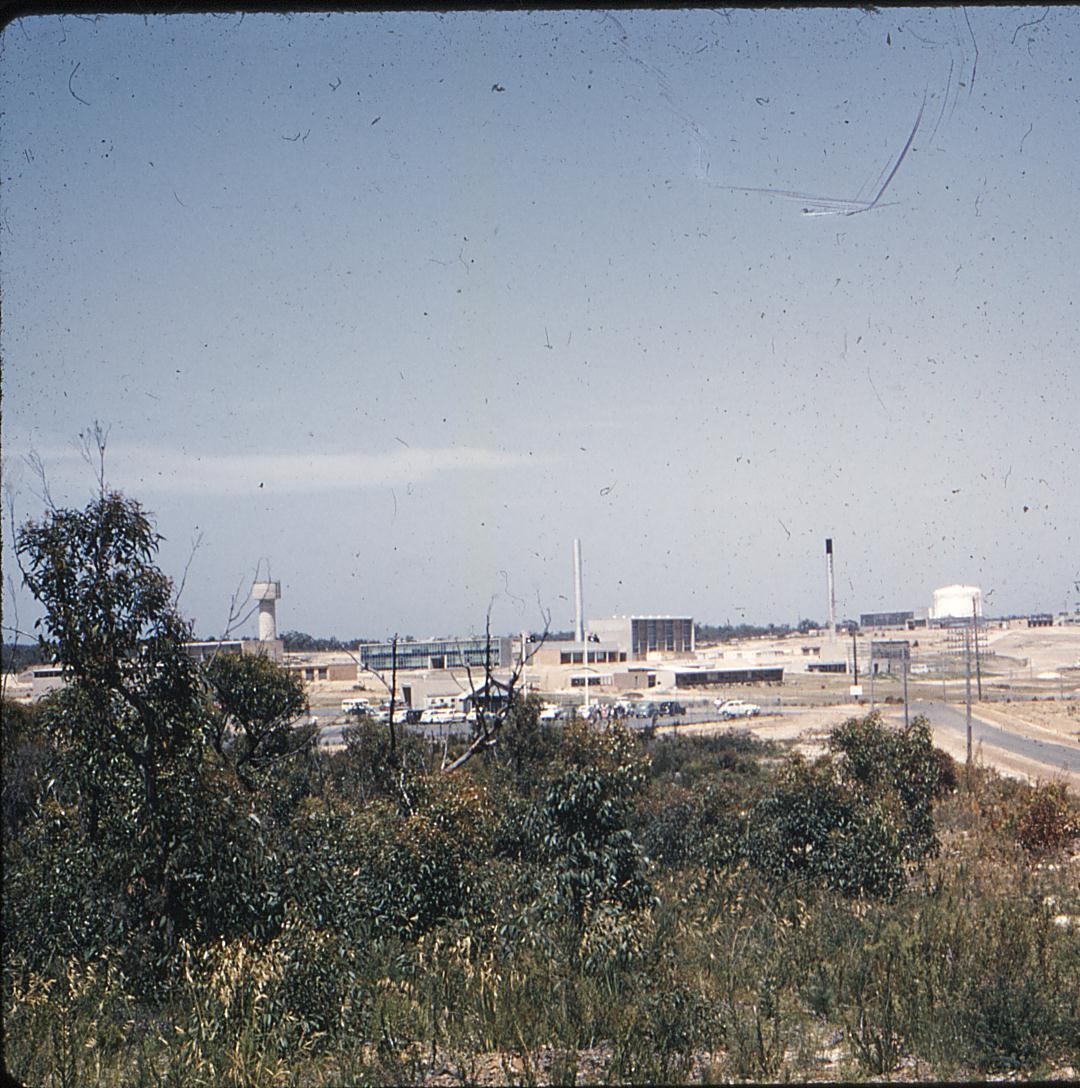

Becoming ANSTO
85 ANU, Melbourne Uni and AAEC setup the National Accelerator Facility
Ted Ringwood’s concept for Synroc
First IBA measurements using a CAS accelerator

Critical Facility (ANSTO Building 53) formally opened by Prime Minister William McMahon
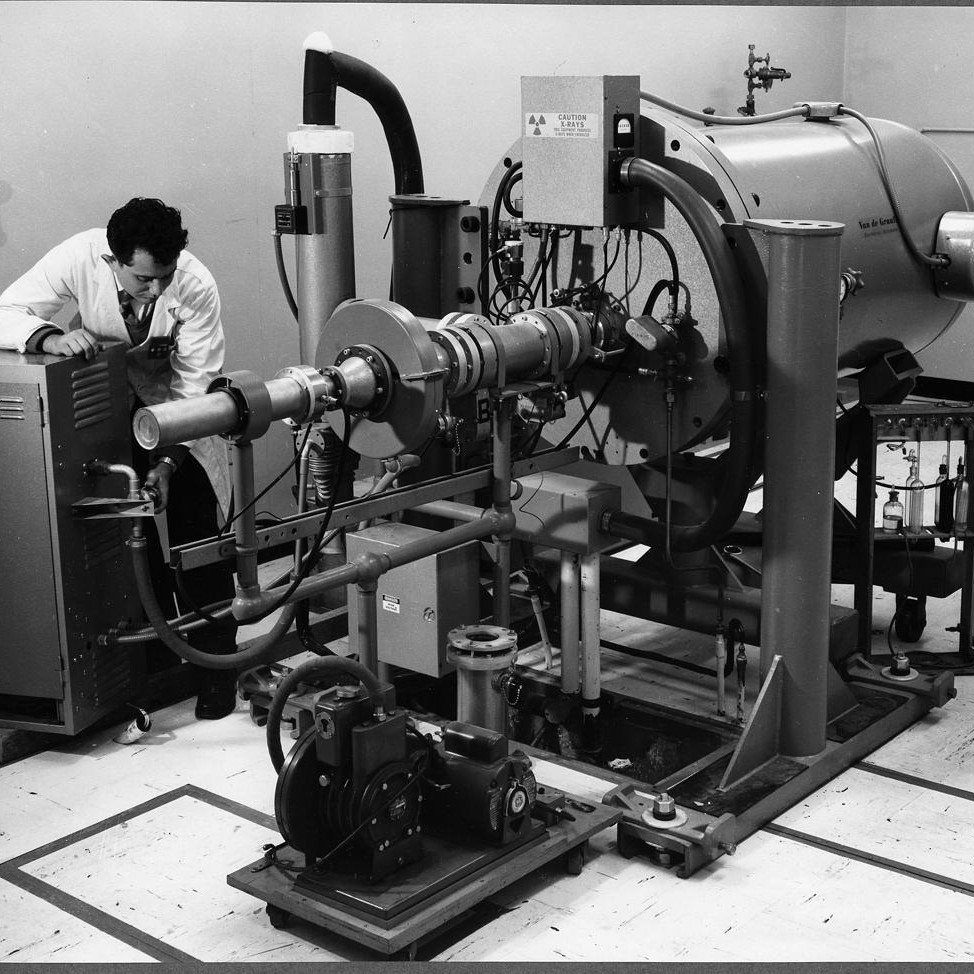

3MV Van de Graaff had 7 beamlines at CAS Facility
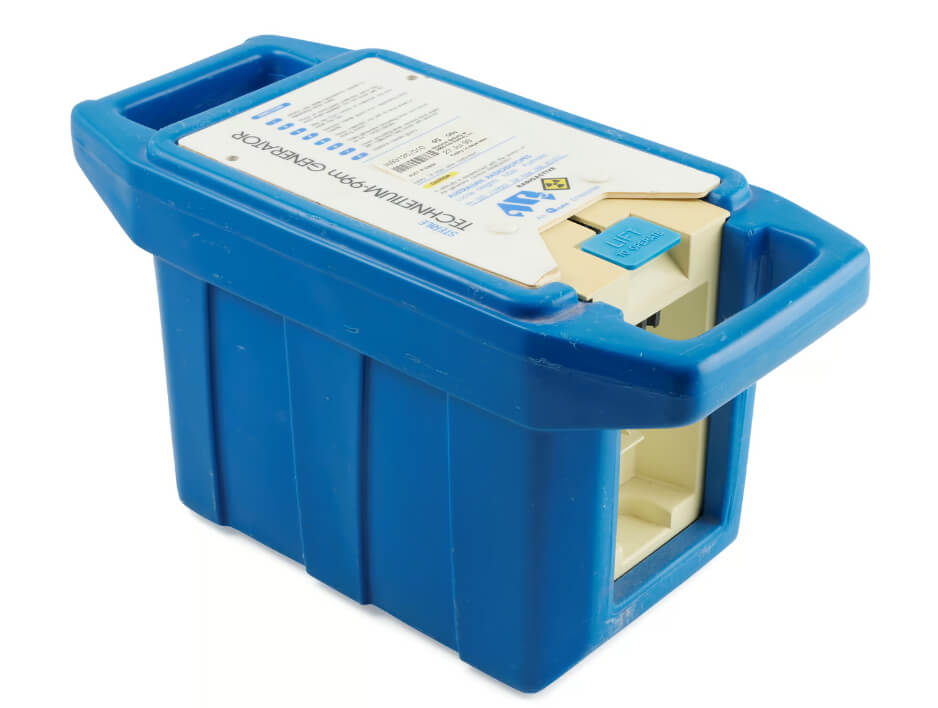

Technetium-99m Gentech Generator enables nuclear medicine
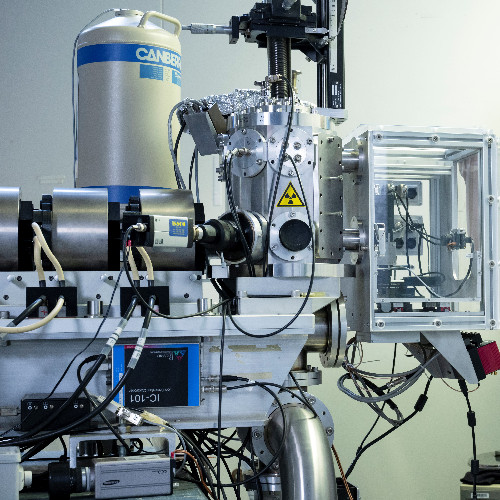
CAS (Centre for Accelerator Science) 64 3MV Acceptance tests completed
Moata reactor operational

HIFAR reactor officially opened by Robert Menzies

Australia supports the formation of the IAEA
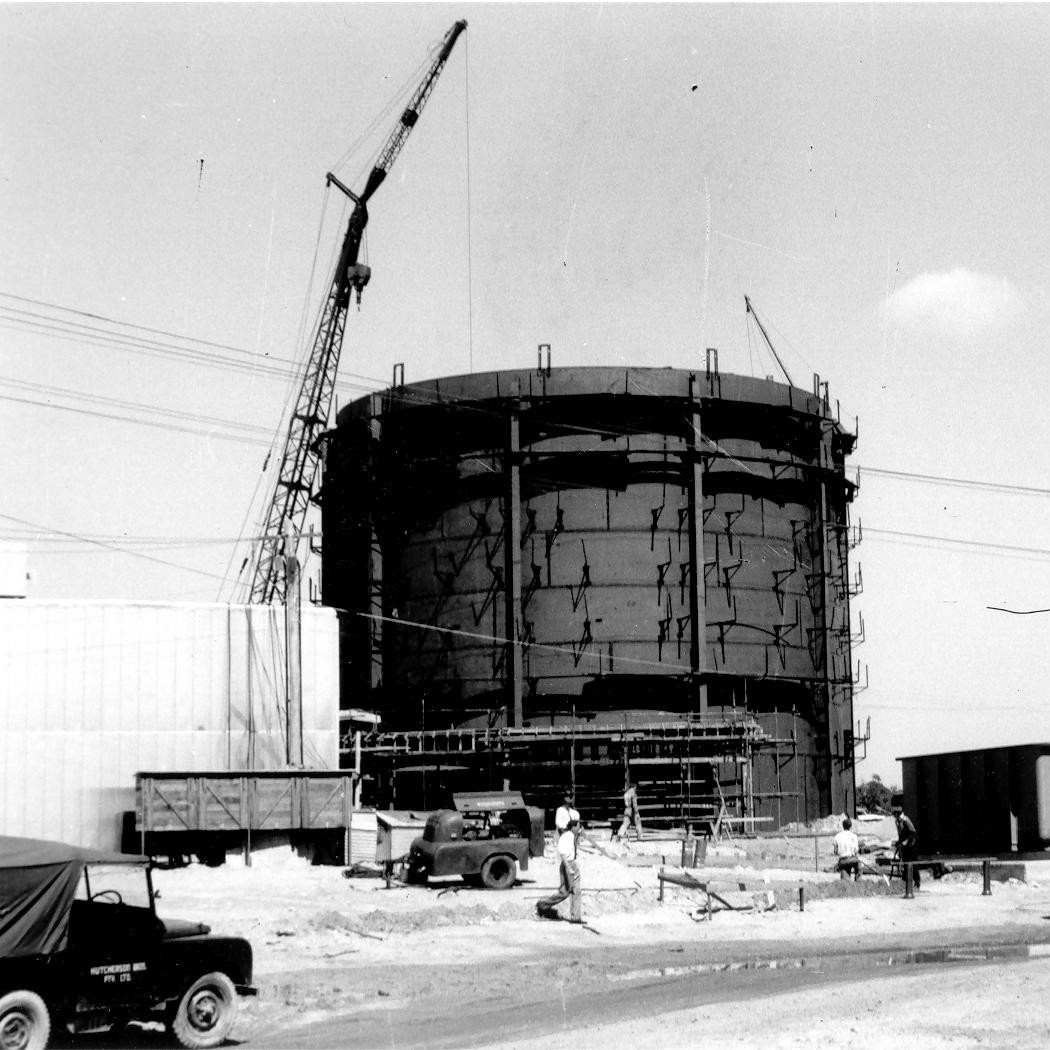

Construction on HIFAR reactor commenced
The Australian Atomic Energy Act came into effect 15 April 1953